🧪THE INTERNATIONAL SYSTEM OF UNITS (SI Units) – Complete, Simple Guide for Students
🎯 Goal: Understand how we measure everything in science using standard units — the SI units.
🧠WHAT IS A UNIT? (Introduction)
Imagine you’re baking a cake 🍰 and the recipe says “2 cups of flour.”
What’s a “cup”? It’s a unit — a way to measure flour.
✅ In science, we measure things like length, mass, time, temperature, etc. using standard units so that everyone around the world can understand and compare results easily.
🔹 Why Do We Measure?
Every time we measure something — a distance, weight, time, temperature — we’re comparing it to a standard. That standard is called a unit.
🧠 Definition:
A measurement = a number + a unit
Example: 5 metres, 2 kilograms, 60 seconds
We don’t need separate units for every physical quantity. Why?
👉 Because most physical quantities are connected (e.g., speed = distance ÷ time), we can build many from just a few basic units.
📏 Key Concepts:
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Measurement | Comparing a quantity with a standard unit |
| Unit | A fixed, agreed way to measure a physical quantity |
| Physical Quantity | Anything we can measure — like mass, length, time, etc. |
| Base/Fundamental Units | Basic units used to define all others |
| Derived Units | Made by combining base units (e.g., speed = metre/second) |
| System of Units | Complete set of base + derived units |
🧠 Think of it like LEGO®:
Base units = LEGO bricks
Derived units = anything cool you build with them!
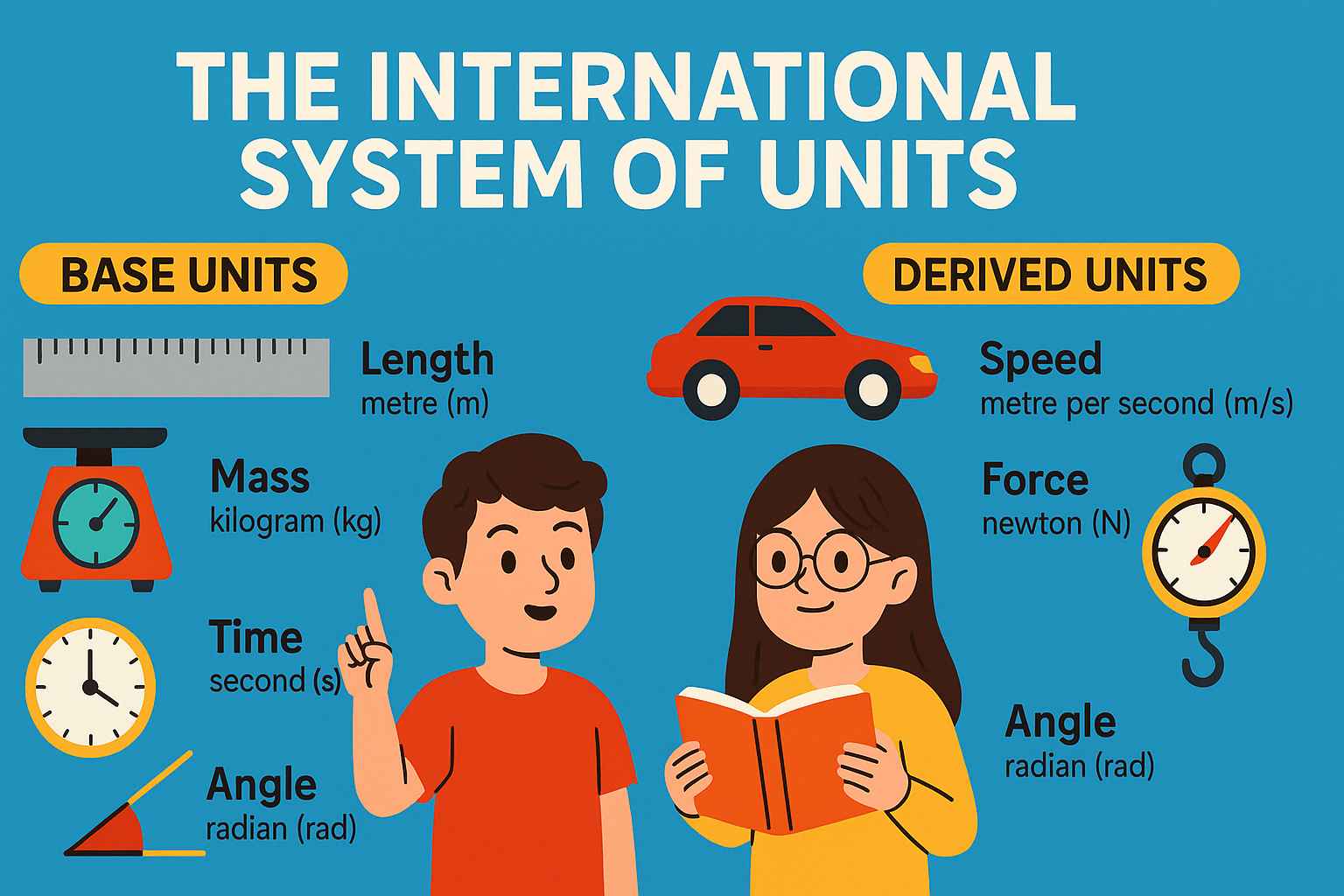
🧱 Types of Units
| Type of Unit | Meaning | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Fundamental (Base) Units | The basic units used to measure base physical quantities | metre, second, kilogram |
| Derived Units | Units formed by combining base units | m/s, newton, joule |
| System of Units | A complete set of base and derived units | SI system, CGS, MKS |
🔁 We only need 7 base units to describe the whole physical world!
🌍 1.2 WHY INTERNATIONAL UNITS? (The SI System)
Long ago, different countries used different units. That was a mess!
Imagine one country using centimetres, another using feet — chaos! 🌀
So scientists agreed on a universal language of measurement:
🌐 The SI System (Système Internationale d’Unités)
🌍 THE INTERNATIONAL SYSTEM OF UNITS (SI)
Earlier, different countries used different systems — it caused confusion:
| System | Length | Mass | Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| CGS | centimetre | gram | second |
| FPS (British) | foot | pound | second |
| MKS | metre | kilogram | second |
To solve this, scientists adopted a universal system:
🏛️ Système Internationale d’Unités (SI) — French for International System of Units
Now, we all use the SI System — it’s neat, logical, and based on decimals (easy for calculations!). It was adopted officially in 1971 and revised in 2018 for better accuracy.
✅ Introduced by: BIPM (International Bureau of Weights and Measures)
✅ Adopted globally in: 1971
✅ Revised in: 2018 for higher precision using universal constants like the speed of light, Planck constant, etc.
✨ SI is used in science, engineering, industry, and even daily life worldwide.
📊 The 7 SI Base Units (As per 2018 Definitions)
| Physical Quantity | Name | Symbol | Defined Using |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length | metre | m | Distance light travels in vacuum in 1/299,792,458 seconds |
| Mass | kilogram | kg | Defined using the Planck constant: 6.62607015×10⁻³⁴ Js |
| Time | second | s | Time taken for 9,192,631,770 cycles of microwave radiation in caesium-133 |
| Electric Current | ampere | A | Defined using charge of electron 1.602176634×10⁻¹⁹ C |
| Thermodynamic Temperature | kelvin | K | Using Boltzmann constant 1.380649×10⁻²³ J/K |
| Amount of Substance | mole | mol | Contains exactly 6.02214076×10²³ entities (Avogadro number) |
| Luminous Intensity | candela | cd | Defined using luminous efficacy of 540 THz light as 683 lm/W |
🧠 Memory Tip:
“My King Took A Long Mango Salad Coldly”
(Metre, Kilogram, Second, Ampere, Kelvin, Mole, Candela)
📝 Note: These definitions are based on fixed physical constants for precision.
❗ You don’t need to memorize the constants — just know they give us very accurate units.
📐 Extra SI Units — Angles (Bonus Units)
Two more units are part of the SI system, used to measure angles, but are dimensionless.
| Quantity | Unit | Symbol | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plane Angle | radian | rad | θ = ds / r |
| Solid Angle | steradian | sr | Ω = dA / r² |
🧠 Visual:
- Radian: Angle made by an arc = arc length ÷ radius
- Steradian: 3D version = surface area ÷ radius²
🧪 Derived SI Units (Built from Base Units)
| Quantity | Unit | Formula | Special Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | m/s | m/s | — |
| Acceleration | m/s² | m/s² | — |
| Force | kg·m/s² | — | newton (N) |
| Energy | kg·m²/s² | — | joule (J) |
| Power | kg·m²/s³ | — | watt (W) |
| Pressure | N/m² | — | pascal (Pa) |
| Frequency | s⁻¹ | — | hertz (Hz) |
| Electric Charge | A·s | — | coulomb (C) |
🧠 Many of these are listed in Appendix A 6.2 & A 6.3 with special names and symbols.
🧠 Important Notes on Mole and Candela
- Mole: Must specify the entity: atoms, molecules, ions, etc.
- Candela: Focuses on how bright a light is in a specific direction using a reference light frequency (540 THz)
⚖️ Other Units Still in Use (Not SI)
Even though SI is the standard, some non-SI units are still used for convenience:
- 📚 Useful Extras You Should Know:
- ✅ Some non-SI units (like minute, hour, litre) are still used — find these in Table 1.2.
- ⚠️ When using mole, always specify the entities (atoms, molecules, etc.).
- 📏 SI uses decimal prefixes like kilo (1000×), milli (1/1000), etc. — See Appendix A2.
- 📐 Follow standard symbols & rules — See Appendices A7 & A8 for guidance.
| Quantity | Common Units |
|---|---|
| Time | minute, hour, day |
| Volume | litre (L) |
| Mass | tonne |
| Energy | calorie |
| Pressure | bar |
See Table 1.2 in your book for more such examples.
📏 SI Prefixes (For Big and Small Quantities)
| Prefix | Symbol | Multiplier |
|---|---|---|
| kilo | k | 10³ |
| milli | m | 10⁻³ |
| micro | µ | 10⁻⁶ |
| mega | M | 10⁶ |
| nano | n | 10⁻⁹ |
📌 Complete list in Appendix A2
✍️ General Rules to Remember (from Appendices A7 & A8)
- Always use correct symbols, not full names in equations (e.g., use
kg, notkilogram) - No plural for units (write
5 kg, not5 kgs) - Leave a space between number and unit (
25 m, not25m) - Never mix units from different systems
🚀 Final Thought
The SI system makes science clear, connected, and universal. Whether you’re in Delhi or Denmark, when you say “1 kilogram,” everyone knows exactly what you mean! 🌍
🌟 Final Recap: Why SI Units Matter
✅ Simple to use (decimal-based)
✅ Universal and accepted worldwide
✅ Based on physical constants — super accurate
✅ Helps scientists, engineers, and even daily life
